DAO Implementation
The Data Access Object (DAO) pattern is a good practice to implement a
persistence layer and it encapsulates data access codes from the
business tier. A DAO object exposes an interface to a business object
and performs persistence operation relating to a particular persistent
entity. Now, we can implement persistence operations like CRUD in a DAO
class with JPA and EntityManager injected by Spring.
@Repository
public class TodoDao {
@PersistenceContext
private EntityManager em;
@Transactional(readOnly=true)
public List<Todo> queryAll() {
Query query = em.createQuery("SELECT t FROM Todo t");
List<Todo> result = query.getResultList();
return result;
}
...
@Transactional
public Todo save(Todo todo){
em.persist(todo);
return todo;
}
@Transactional
public Todo update(Todo todo){
todo = em.merge(todo);
return todo;
}
@Transactional
public void delete(Todo todo){
Todo r = get(todo.getId());
if(r!=null){
em.remove(r);
}
}
}
- Line 1: We register
TodoDaoas a Spring bean with@Repositorybecause it is a DAO class according to Spring's suggestion. - Line 4: As Spring manages our entity manager factory, it can
understand
@PersistenceContextand inject a transaction scopeEntityManagerfor us. Hence, we don't need to createEntityManagerby our own. - Line 7: We have enabled Spring's declarative transaction management
so that we can apply
@Transactionalon a methods.
After completing DAO classes, we can inject them to our service class
with Spring's @Autowired because they are all Spring beans.
@Service("todoListService")
@Scope(value="singleton",proxyMode=ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS)
public class TodoListServiceImpl implements TodoListService {
@Autowired
TodoDao dao;
public List<Todo>getTodoList() {
return dao.queryAll();
}
...
}
Completing the above steps, we have created a dependency relationship among the controller, service, and persistence classes as follows:
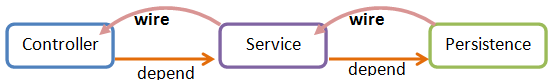
Each of these classes encapsulates cohesive functions and has decoupled relationships with others. You can easily expand the architecture by adding more classes or create dependencies between two layers.
You can visit http://localhost:8080/zkessentials to see the result.